STAMP ISSUES RELATED TO ICAO (1984-1985)
Libya : 40th Anniversary of ICAO
|
Issue date: 07/12/1984
|
|
|
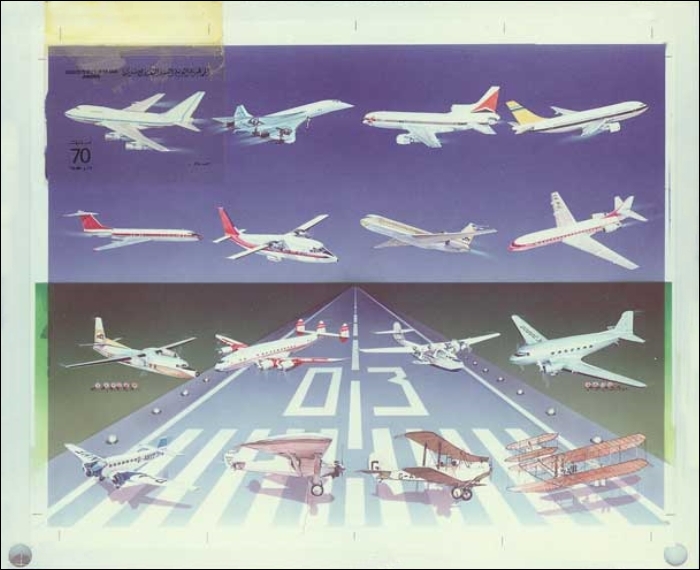
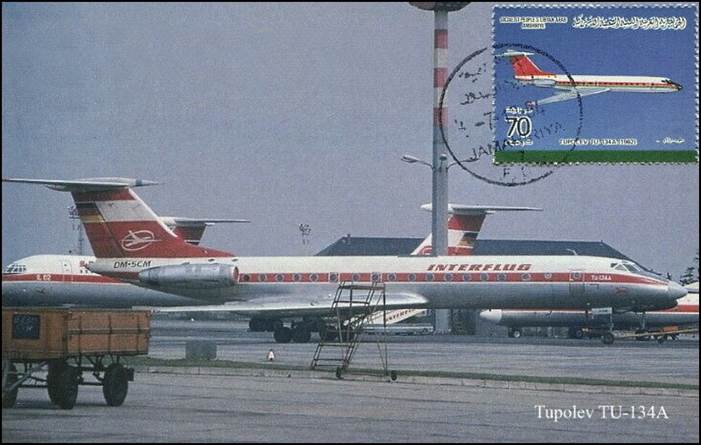
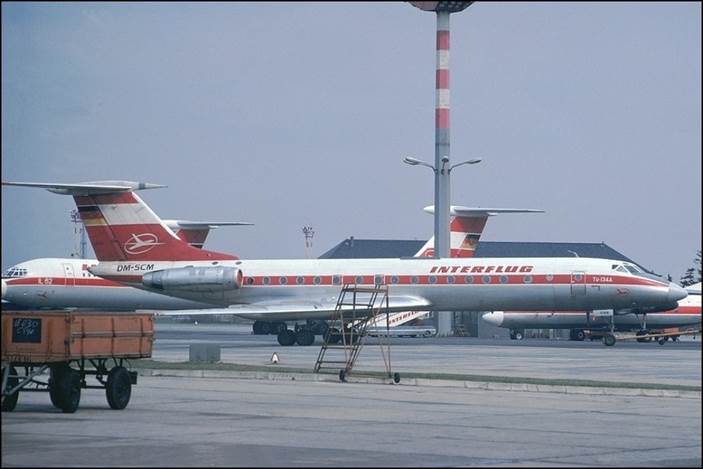
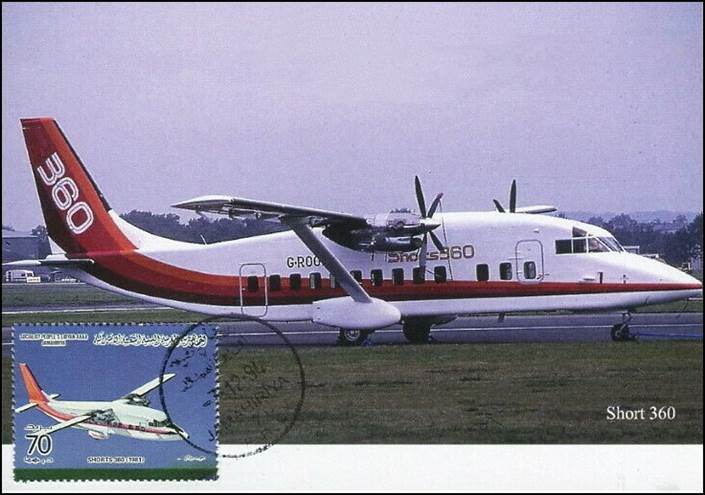
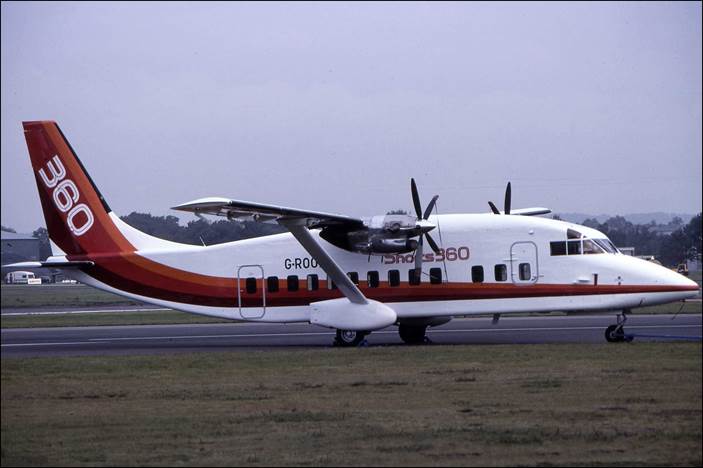
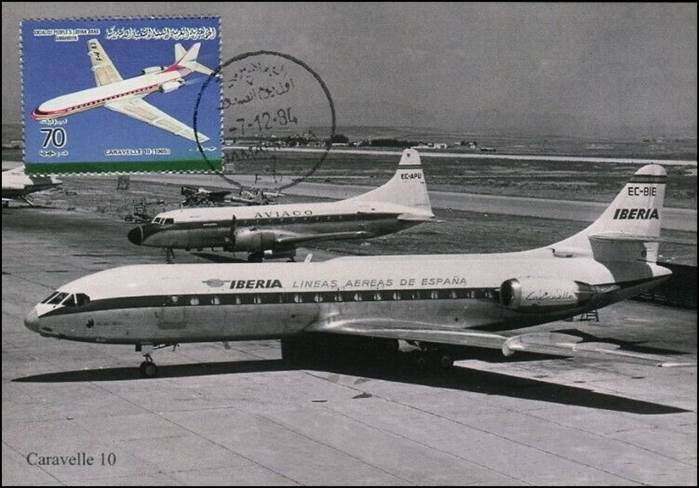
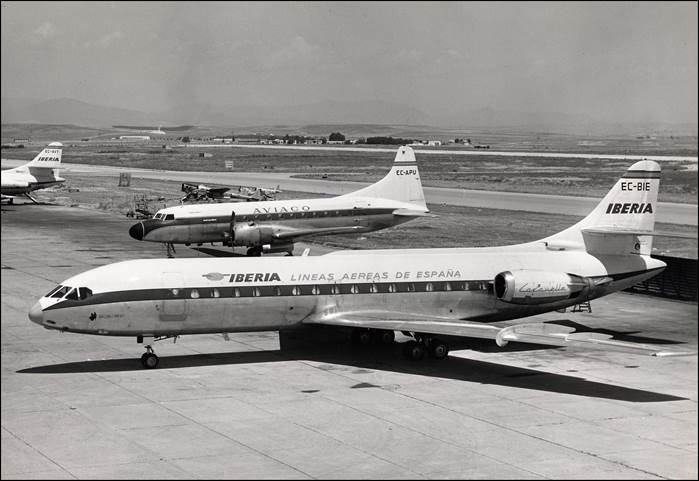
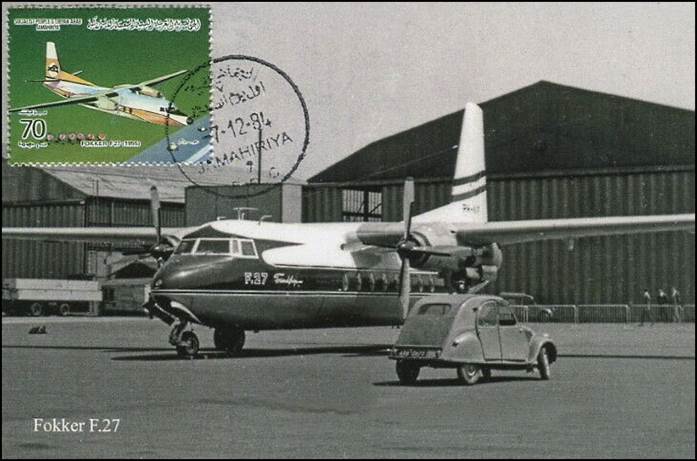
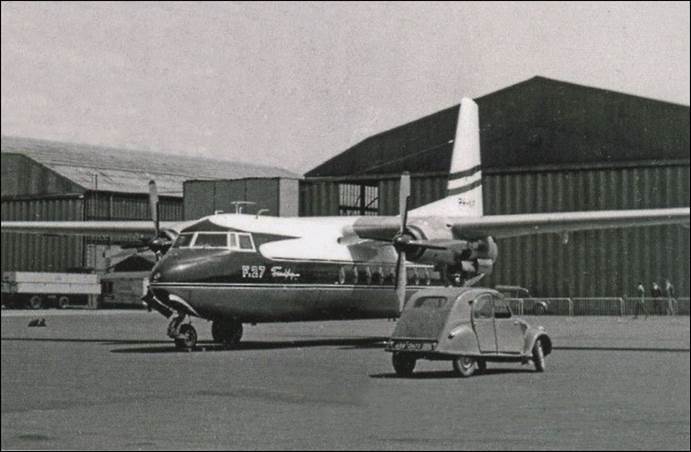
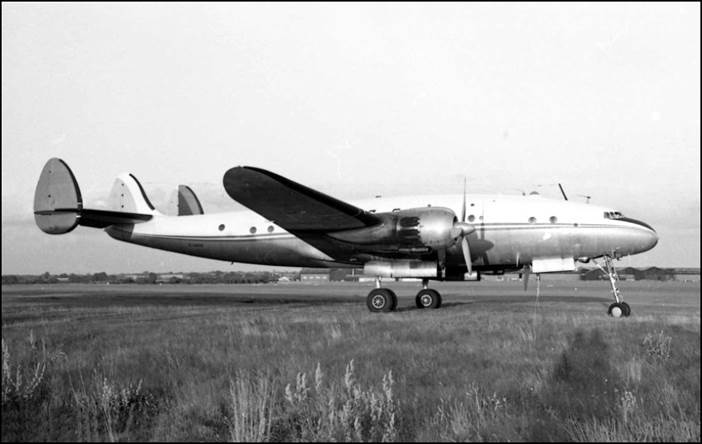
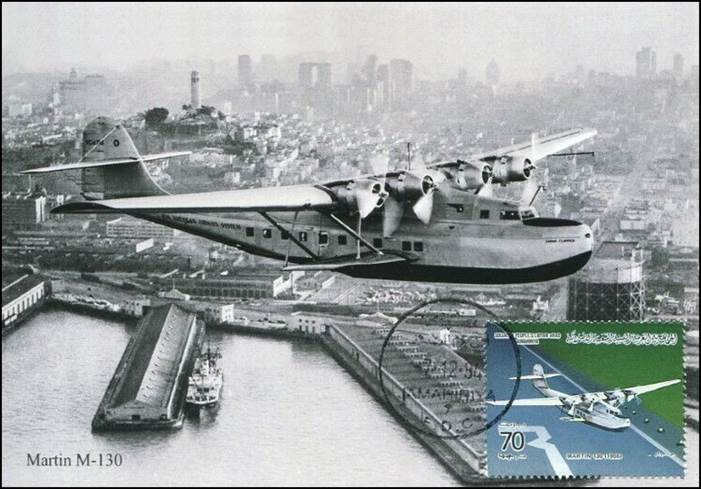
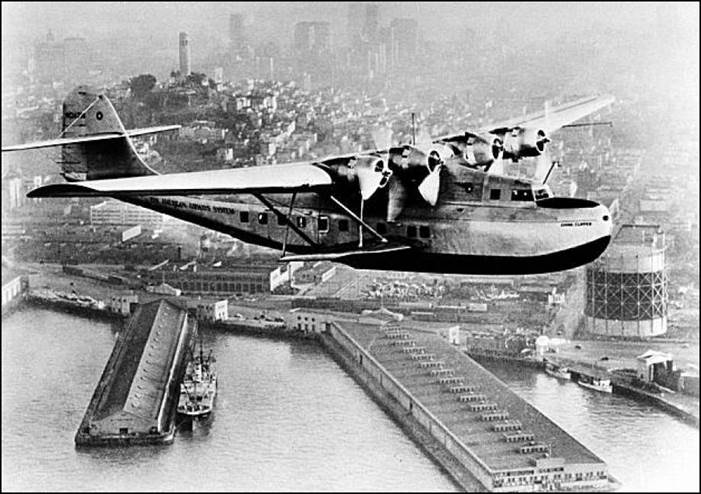
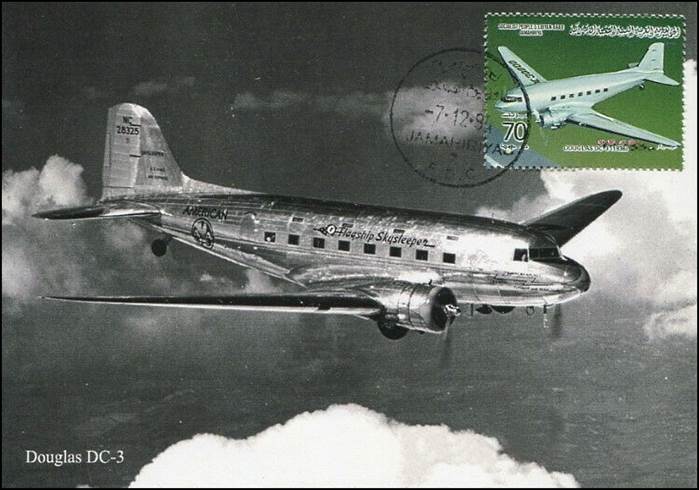
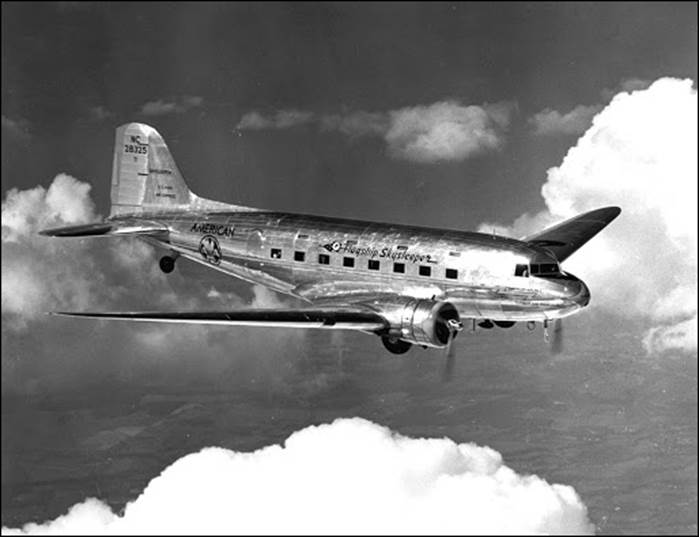
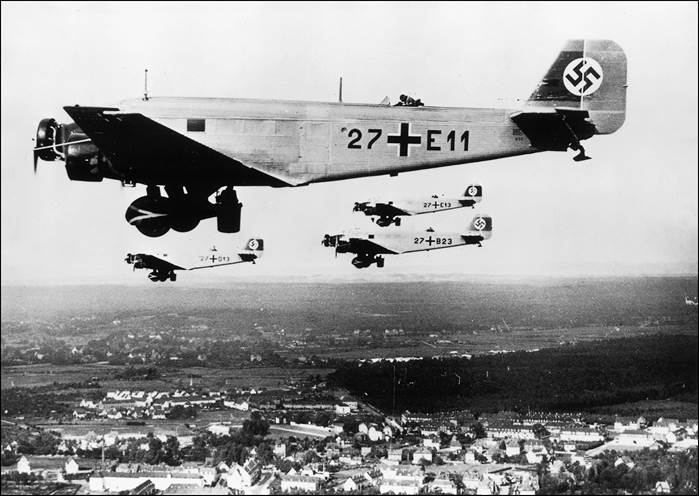
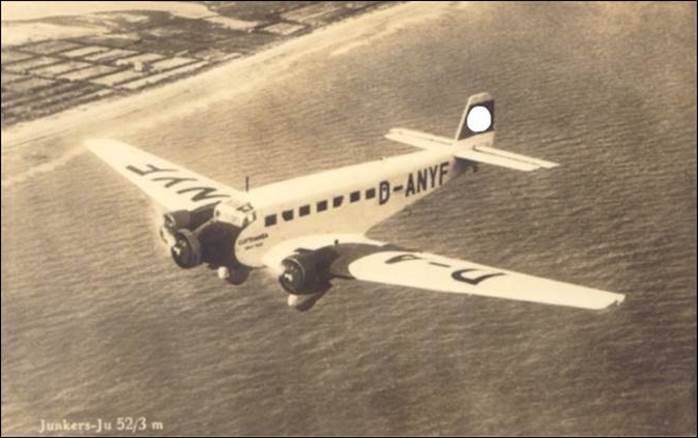
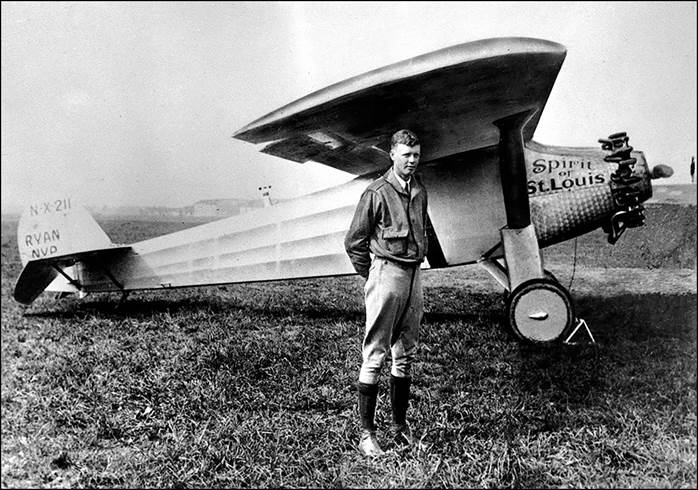
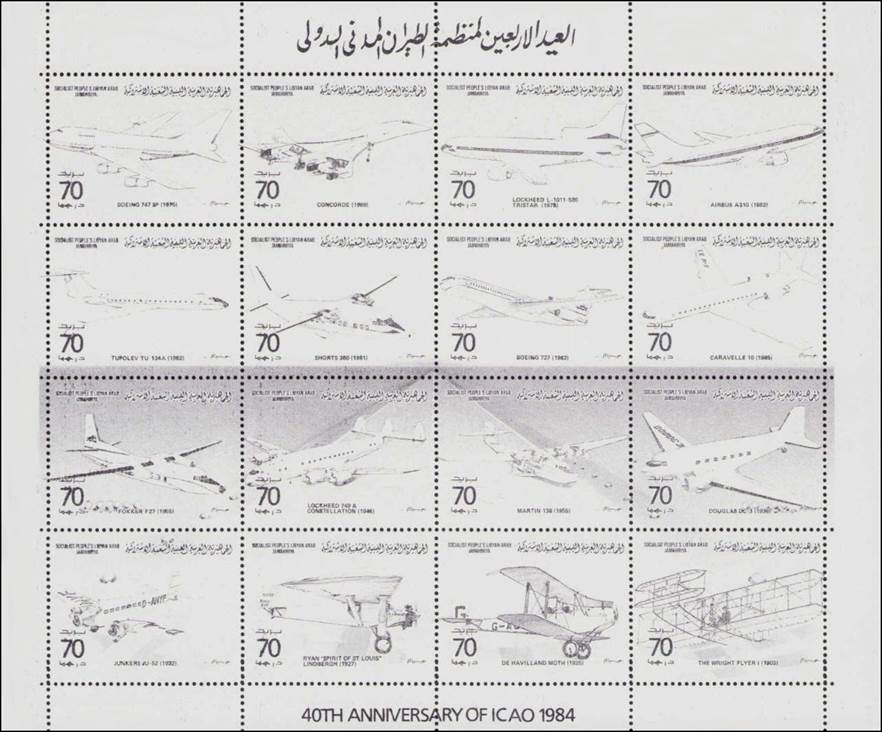
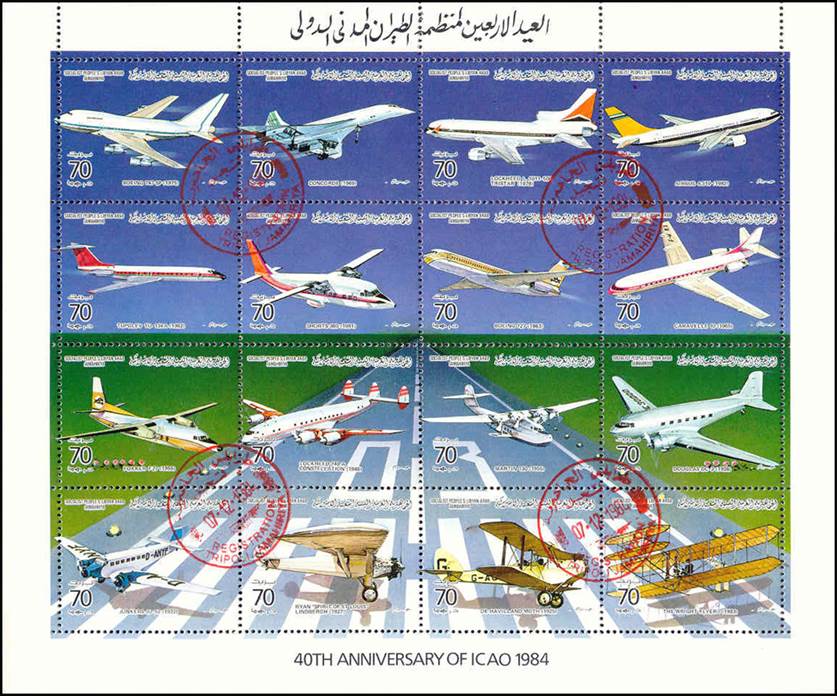
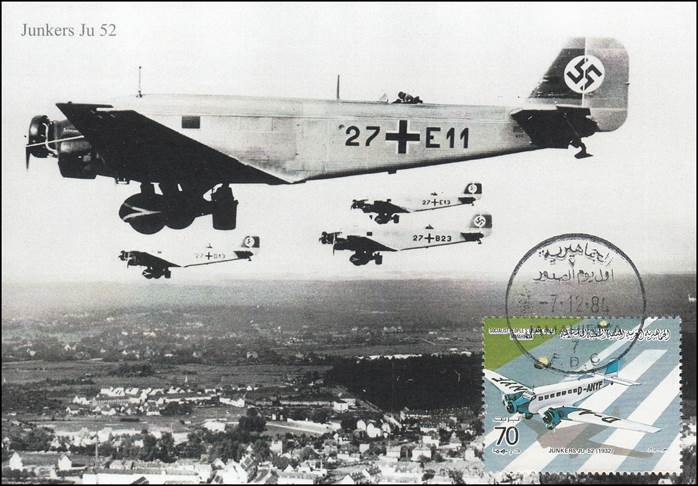
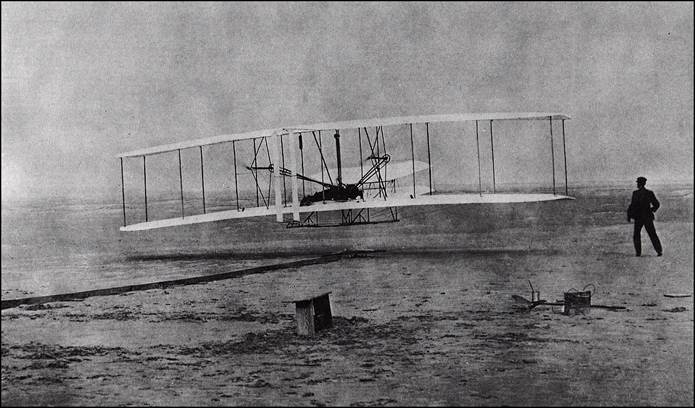
This issue was printed in sheets of 16 stamps (4x4), the backgrounds of the stamps forming an overall design of a runway. Details of the stamps, from left to right and top to bottom: 1. Boeing 747-SP94 (1975); 2. Concorde (1969); 3. Lockheed L-1011-500 Tristar (1978); 4. Airbus A310-203 (1982, registered F-WZLI); 5. Tupolev Tu‑134A (1962); 6. Short 360 (1981); 7. Boeing 727‑100 (1963); 8. Sud Aviation SE 210 Caravelle 10R (1965), registered F-WKJ? (as indicated on the right wing) in France; 9. Fokker F‑27 Friendship (1965); 10. Lockheed L-749A Constellation, registered G-ASYF (1946); 11. Martin M‑130 flying boat (1955); 12. Douglas DC‑3 (1936); 13. Junkers tri-motor Ju 52/3m (the 1m version first flew on 7 March 1932 as a freighter) of Lufthansa, registered D‑ANYF (named "Erich Pust") in Germany. Built in 1935, this aircraft was eventually pressed into service by the Luftwaffe during 1939 and destroyed in 1941;14. Lindbergh's Spirit of St. Louis (1927) registered N-X-211 (for "experimental") in the USA (officially known as the Ryan NYP for New York to Paris); 15. de Havilland D.H.60 Moth (1925), registered G-EBLV in Great Britain; 16. Wright Flyer 1 (1903).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uncut sheet (see missing perforations in lower part of the selvage).
|
|
|
Imperforate sheet.
|
|
|
Chromalin Artist Proof (imperforate).
|
|
|
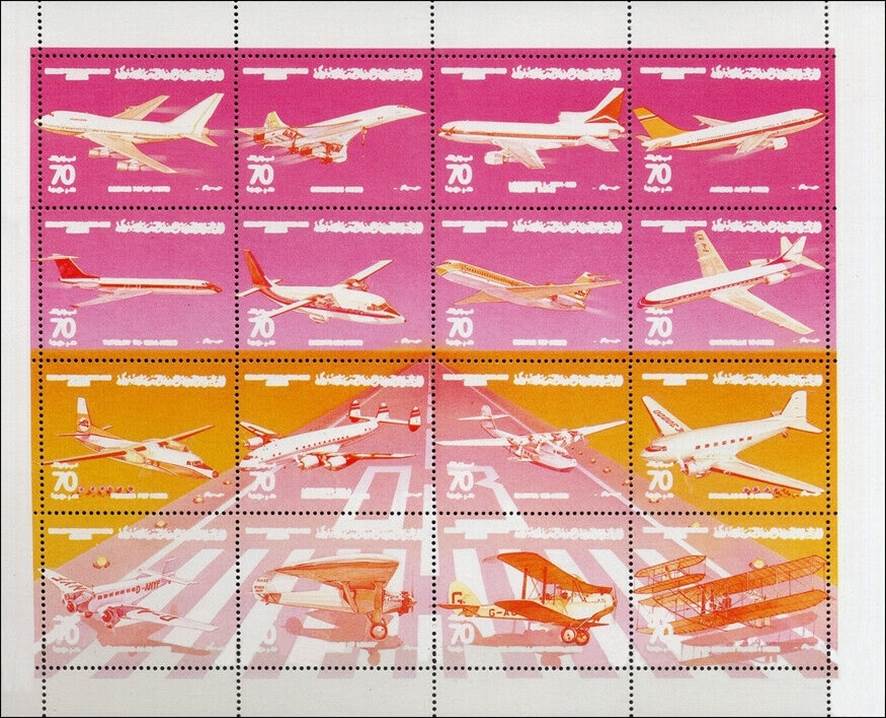
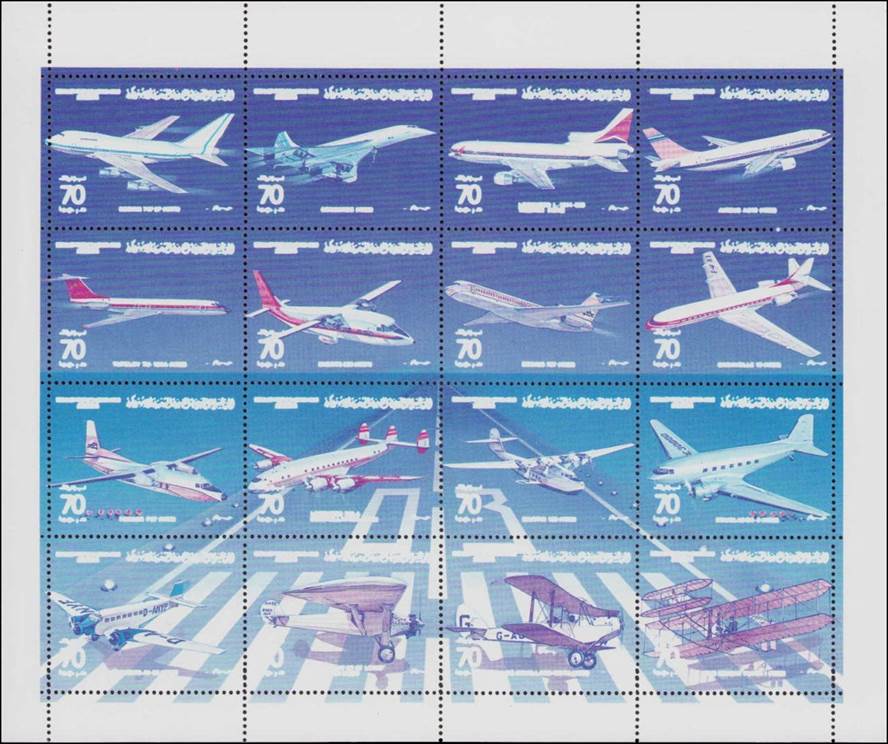
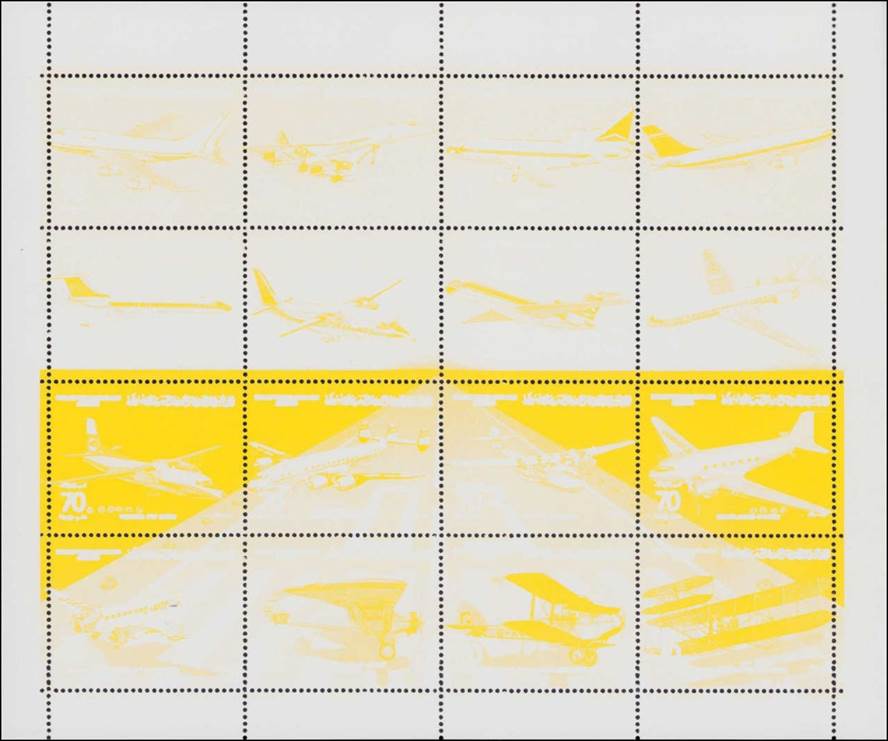
Picture with eight color test perforated sheets (see enlarged pictures below, from left to right, top to bottom).
Eight color test sheets.
|
|
|
Presentation folder of this issue.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First day of issue with red-round postmark for registered mail: 07-12-1984 / REGISTRATION / TRIPOLI JAMAHIRIYA.
|
|
|
First day of issue with red-round postmark for registered mail: 07-12-1984 / REGISTRATION / TRIPOLI JAMAHIRIYA. Error (freak): the plate with the letters of the postmark is inverted; however, the date is correct.
Error: Correct cancel:
|
|
|
The miniature sheet was split into four blocks of four stamps for the First Day Covers (FDC). The cachet shows the emblem of the Posts & Telecommunications of Libya.
|
|
|
Second set of First Day Covers, with another design in the cachet.
|
|
|
16 FDCs, one stamp per cover. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
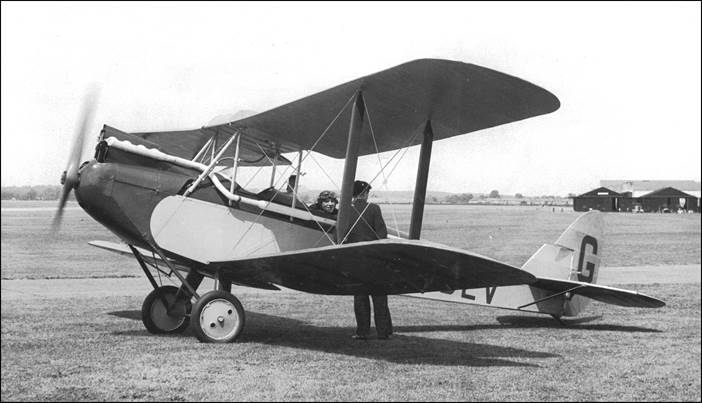
Postal Stationery with pre-printed stamp 200 dirhams (de Havilland D.H.60 Moth, 1925, registered G-Axx (?) in Great Britain) issued on 1 September 1986 to encourage mass sport (Public sport is for all the masses). The back side is blank. Original card without stamps.
|
|
|
The 16 stamps of the miniature sheet (split into four blocks of four stamps) were reutilized on the above preprinted card. First Day cancel dated 1 September 1986.
|
|
|
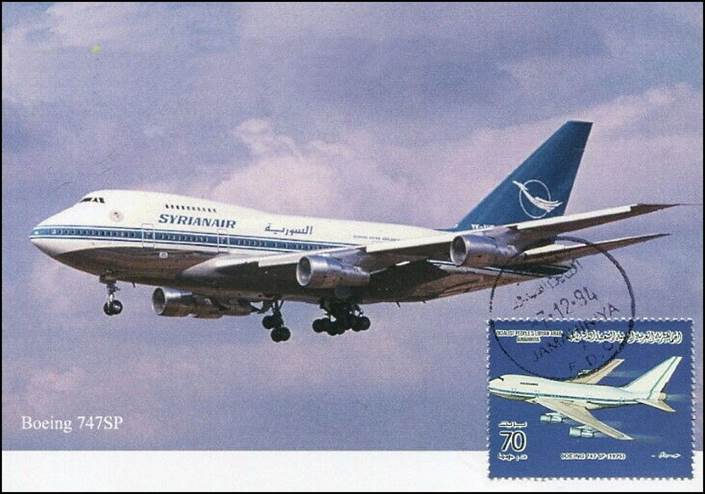
Sixteen maximum cards. Whenever available, the original pictures are displayed to provide full details.
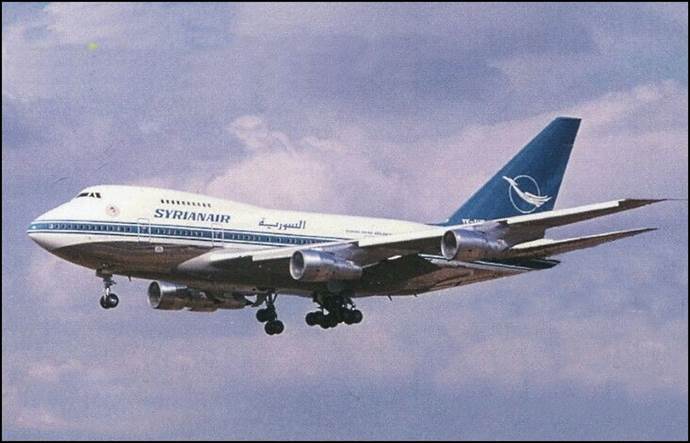
Boeing 747SP-94 of SyrianAir in landing position, registered either YK-AHA or YK-AHB. The Boeing 747SP (SP for Special Performance) is a shortened version of the Boeing 747 widebody airliner, designed for a longer range. Boeing needed a smaller aircraft to compete with the DC-10 and L-1011 trijet widebodies, introduced in 1971/1972. The 747SP was the longest-range airliner available until the 747-400 entered service in 1989. Despite its technical achievements, the SP never sold as well as Boeing hoped. Increased fuel prices in the mid-1970s to early 1980s, the SP's heavy wings, high cost, and reduced capacity, and the increased ranges of forthcoming airliners were some of the many factors that contributed to its low sales. A fleet renewal program was launched in 1975 as the Syrian Arab Airlines ordered three brand-new Boeing 727-294s and two Boeing 747SPs delivered in 1976. Awaiting the delivery of its new planes, the airline leased Boeing 707s in order to improve its service offer. In all, two Boeing 707-420s and six Boeing 707-320s were leased in (respectively from British Airtours and British Midland Airways) at various times between 1974 and 1976 and were used to reinforce frequencies and add new destinations to the network. The two jumbo jets were ordered with the intention of operating trans-Atlantic services to New York. To this effect, a joint agreement with Alia-The Royal Jordanian Airline was anticipated, but never materialized. Therefore, SyrianAir started its Boeing 747SP operations on 1 June 1976 on the Damascus-Munich-London route. The “SyrianAir” acronym was officially adopted on 11 November 1975 in anticipation of the delivery of the new Boeing fleet and in order to generate a more modern and international image. However, the legal and official title continued to be “Syrian Arab Airlines”.
Original picture of the above. |
|